Process modeling essentials

Introduction
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a widely used standard for visualizing, documenting, and optimizing business processes. However, many professionals—whether beginners or experienced modelers—often have questions about its usage, best practices, and real-world applications.
Here are some of the most FAQs about BPMN. We’ll cover key concepts, challenges, and tips for creating effective process models. Whether you want to improve your understanding of BPMN symbols, refine your process diagrams, or troubleshoot modeling issues, this guide provides clear and practical answers to help you navigate BPMN with confidence.
What is BPMN?
BPMN is short for Business Process Model and Notation. It is a standardized graphical representation for specifying business processes in a workflow. It provides a set of symbols and rules to create process diagrams that are easily understandable by all business stakeholders, including analysts, developers, and managers.
Key components of a BPMN diagram?
A BPMN diagram consists of several core components:
Flow objects: events, activities, and gateways that define the behavior of the process.
Connecting objects: sequence flows, message flows, and associations that link flow objects.
Swim lanes: pools and lanes that organize activities based on participants or departments.
Artifacts: data objects, groups, and annotations that provide additional information.
What version of BPMN is currently supported?
The most widely adopted version is BPMN 2.0, which introduced significant enhancements compared to previous versions. BPMN 2.0 includes a more comprehensive set of modeling elements and improved execution semantics.
Capabilities of BPMN
BPMN is a powerful standard for modeling processes, enabling clear communication and efficient workflow management. It standardizes workflows, supports decision making with gateways, and integrates with IT systems. It helps spot bottlenecks, improve collaboration with swimlanes, and manage exceptions with events.
BPMN excels in visualizing complex processes, offering a standardized approach for business analysts and stakeholders. For simpler workflows, consider using flowcharts to maintain clarity. When dealing with highly intricate processes, break them down into manageable BPMN sub-diagrams to enhance readability. To maximize BPMN's effectiveness, invest in training your team. This will ensure everyone can leverage its powerful communication capabilities, fostering better collaboration and process understanding across your organization.
What is a simple example of a BPMN diagram?
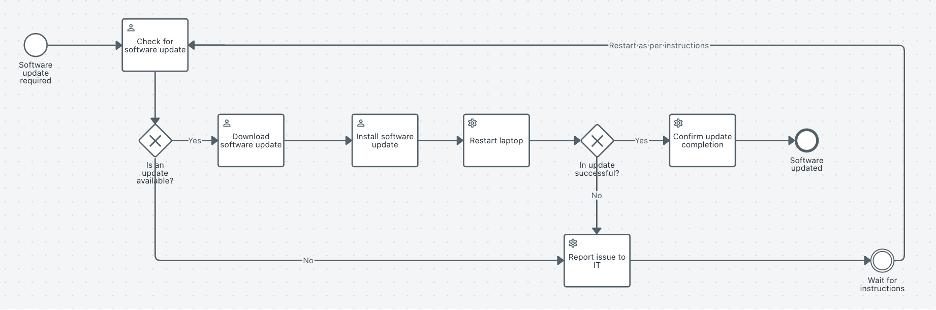
This BPMN 2.0 diagram follows a structured single swim lane process where a process modeler updates the software on a company-issued laptop. Below is a breakdown of the process using BPMN elements so you can understand the model comprehensibly.
BPMN elements in the Diagram:
1. Start event
Symbol: thin-outlined circle
Label: "software update required"
Purpose: The process begins when a software update is needed
2. Task: "Check for software update"
Symbol: rounded rectangle/task
Type: user task (process modeler performs this manually)
Purpose: The process modeler checks if an update is available on the laptop.
3. Exclusive Gateway (XOR): "Is an update available?"
Symbol: diamond shape/decision point
Type: exclusive gateway (XOR)
Purpose: determines whether an update is available.
✅ If yes → proceed to download the update.
❌ If no → notify IT and wait for further instructions.
4. Task: "Download software update"
Symbol: rounded rectangle/task
Type: user task
Purpose: the process modeler downloads the required update files.
5. Task: "Install software update"
Symbol: rounded rectangle/task
Type: user task
Purpose: The modeler installs the update on the laptop.
6. Task - "Restart laptop"
Symbol: rounded rectangle/task
Type: user task
Purpose: The laptop is restarted to apply the software update.
7. Exclusive Gateway (XOR) - "Is update successful?"
Symbol: diamond shape decision point
Type: exclusive gateway (XOR)
Purpose: checks if the update was applied successfully.
✅ If yes → proceed to confirm update completion.
❌ If no → report the issue to IT.
8. Task - "Confirm update completion"
Symbol: rounded rectangle/task
Type: user task
Purpose: The employee verifies and confirms that the update was successful.
9. Task - "Report issue to IT"
Symbol: (rounded rectangle/task)
Type: user task
Purpose: If the update fails, the process modeler reports the issue to IT for further troubleshooting.
10. End event — "Laptop updated"
Symbol: thick-outlined circle
Label: "Laptop updated"
Purpose: The process ends once the update is either completed or reported to IT.
Frequently asked questions about BPMN
How do I create a BPMN diagram?
Create your BPMN diagram in our new process modeling canvas. You can import your BPMN models into UiPath Maestro, currently in public preview, to implement, operate, and optimize your business processes. See our detailed documentation here.
Is it possible to reference another process within a BPMN process flow?
Yes, BPMN allows referencing other processes using call activities. A call activity is a type of activity that indicates a point in the process where a predefined process or subprocess is used. This promotes reusability and simplifies complex process models.
Can BPMN be integrated with other modeling standards?
Yes, BPMN is often used alongside other standards such as Unified Modeling Language (UML) and DMN (Decision Model and Notation) to provide a comprehensive view of business processes and decision logic.
What is the file type of BPMN?
BPMN diagrams are saved with.BPMN file extension and have XML format.
Can BPMN help automate my daily tasks?
Yes! BPMN is often integrated with automation tools to reduce manual work, speed up approvals, and ensure consistent workflows for tasks like reporting, document approvals, and system access requests.
How do I read a BPMN diagram?
A BPMN diagram consists of tasks (rectangles), decisions (diamonds), start and end points (circles), and connectors (arrows) showing the workflow’s sequence. Some diagrams also include swimlanes to show who is responsible for each step. You can refer to the example shared above to understand the basic components of a BPMN diagram.
Does BPMN require coding knowledge?
No, BPMN is a visual tool that developers use for process automation. Other entities only need to read diagrams to understand how workflows function.
How is BPMN different from a regular flowchart?
Unlike flowcharts, BPMN follows a global standard and includes specific elements like events, gateways, and swim lanes to model real-world business processes with more accuracy.
Good luck modeling!
UiPath Maestro, our new product to model, implement, operate, monitor, and optimize your long-running processes, is now in public preview.
If you're a UiPath customer, you can try Maestro via UiPath Automation Cloud™. After you have access to the Maestro service, select "Get started" to open the modeling canvas.
If you're not an Automation Cloud customer, you can access Maestro via a free trial.
Principal Product Manager, UiPath
Get articles from automation experts in your inbox
SubscribeGet articles from automation experts in your inbox
Sign up today and we'll email you the newest articles every week.
Thank you for subscribing!
Thank you for subscribing! Each week, we'll send the best automation blog posts straight to your inbox.



